Likely 2023 BECE Integrated Science Questions With Full Answers
Likely BECE 2023 Integrated Science (Questions With Full Answers)
Enhancing student performance through quality assessment
BECE Social Studies Questions For 2023 Candidates is one of the important subjects that candidates need to pass. Integrated Science is a core subject meanings you have to pass to stand a chance of progressing into the SHS.
Do not open this booklet until you are told to do so. While you are waiting, read and observe the following instructions carefully. Write your name and index number in ink in the spaces provided above.
This booklet consists of two papers; I and II. Answer Paper 2 which comes first in your answer booklet and Paper 1 on your Objective Test answer sheet. Paper 2 will last for 1 hr after which the answer booklet will be collected. Do not start the Paper until you are told to do so. Paper 1 will last 45 MINS .
INTEGRATED SCIENCE 2
This is a 2023 BECE Integrated Science Mock With Full Answers from Ghana Education News for all BECE candidates. This is s paper for revision and can be used by schools as mock examination questions for candidates.
ESSAY [100 marks]
1 ¼ hours
This paper is in two sections: A and B. Answer Question 1 in section A and any other four questions in section B
Credit will be given for clarity of expression and orderly presentation of material.
SECTION A
[40 marks]
Answer all of Question 1
- (a) The funnels in the diagram below contain equal amounts of different types of soils labelled K, L and M. Equal volumes of water were poured onto each soil at the same time and allowed to drain for 20 minutes.
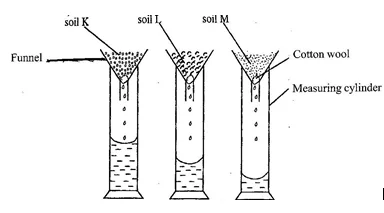
Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow
- What is the aim of the experiment? [2 marks]
- Which soil has the highest rate of drainage? [1 mark]
- Which soil has the highest water retention capacity? [1 mark]
- Which soil is most likely to lose water and dry faster after rainfall? [1 mark]
- Which soil is most likely to be waterlogged after rainfall? [1 mark]
- Which of the soil types would be suitable for maize cultivation? [1 mark]
(b) The diagram below illustrates hazard symbols labelled I, II, III and IV.
Study the diagram carefully and answer the questions that follow.
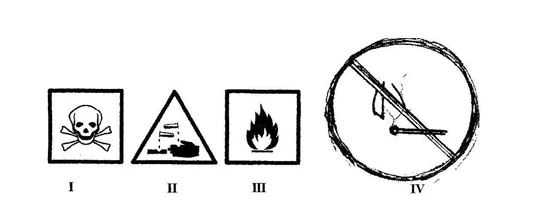
- What does each of the symbols labelled I, II, III and IV represent?
- Name one substance each that is associated with:
(α) I;
(β) II;
(γ) III. [3 marks]
- Name a place where the hazard symbol labelled IV is often displayed [1 mark]
- Which of the symbol(s) is / are found on chemical containers? [3 marks]
The diagrams below are illustrations of devices used to do work easily
Study the diagrams and answer the questions that follow
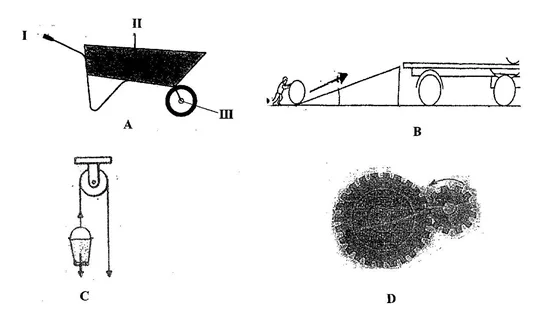
- Give a general name for the devices. [1 mark]
- Identify each of the devices labelled A, B, C and [4 marks]
- Name the parts labelled I, II and III of device A when it is considered as a lever.
[3 marks]
- What does the arrow represent in the device labelled B? [1 mark]
- Name the type of work done with each of the devices labelled:
(α) C;
(β) D; [2 marks]
(d) The diagram below illustrates the digestive system in humans.
Study the diagram carefully and answer the questions that follow
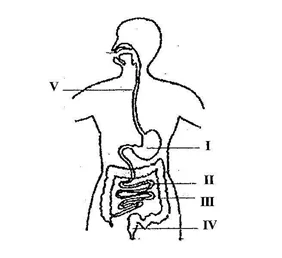
- Name each of the parts labelled I, II, III, IV and V [5 marks]
- Name the part(s) of the digestive system where
(α) digestion of food substances occur
(β) digested food is absorbed into the bloodstream [3 marks]
- Name the end-products of the digestion that is absorbed into the bloodstream
[3 marks]
PART II
[60 marks]
Answer four questions only from this section
- (a) (i) What is germination of seed?
(ii) State two conditions necessary for the germination of seed.
(b) State four methods used in identifying farm animals
(c) Explain why it is easier to cut a piece of yam with a sharp knife than with a blunt knife
(d) State three differences between a metal and a non-metal.
- (a) (i) What is technology?
(ii) State two differences between science and technology. [4 marks]
(b) Draw potassium atom and show the distribution of electrons in its shells.
[K = 19] [4 marks]
(c) What energy transformations take place in each of the following activities?
(i) Using a flashlight battery to produce light in a bulb.
(ii) Using a microphone to address a gathering. [4 marks]
(d) List three components of soil. [3 marks]
- (a) (i) Explain the term electromagnetic
(ii) Given a nail, insulated wire, key (or switch) and a battery, show by means of a circuit diagram how the nail can be magnetized.
(b) List three symptoms of malaria.
(c) State three ways of keeping the environment clean.
(d) Write down the names of the new substances formed when the following compounds react: (i) Ammonia and dilute hydrochloric acid;
(ii) Sodium hydroxide and dilute hydrochloric acid;
(iii) Calcium carbonate and dilute hydrochloric acid.
- (a) (i) State the difference between an opaque object and a translucent objec
(ii) Give one example each of an opaque and a translucent material.
(b) (i) What is the importance of seed dispersal?
(ii) Name two types of fruits and state their mode of dispersal.
(c) (i) What is recycling?
(ii) Give two advantages of recycling of materials
(iii) List three recycled products in Ghana.
- (a) (i) What is weather?
(ii) State two differences between weather and season [4 marks]
(b) State the composition of each of the following alloys;
(i) steel;
(ii) stainless steel [3 marks]
(c) List four benefits of vegetables to humans [4 marks]
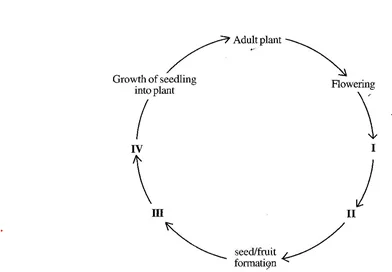
(d) The diagram below is an illustration of life-cycle of a flowering plant.
Name each of the stages labelled I, II, III and IV [4 marks]
INTEGRATED SCIENCE 1
OBJECTIVE TEST
45 minutes
1. Which of the following is a liquid?
A. iron
B. mercury
C. brass
D. gold
2. Photosynthesis in plants requires chlorophyll, sunlight, water and
A. oxygen
B. carbon dioxide
C. steam
D. hydrogen
3. Why is it bad to throw faeces into rivers? Because
A. other people collect drinking water from them
B. it changes the colour of the river
C. it causes hardness of the water
D. the faeces cannot dissolve in the water
4. Steel is an alloy of
A. Iron and Carbon
B. Zinc and Copper
C. Tin and Copper
D. Iron and Zinc
5. Which of the following is not a communicable disease?
A. smallpox
B. chicken pox
C. influenza
D. pneumonia
6. A mixture of sugar and water can be separated by
A. filtration
B. evaporation
C. decantation
D. distillation
7. On the moon, there are large holes called
A. valleys
B. gullies
C. spurs
D. craters
8. The purpose of vaccination is to
A. replace poisoned tissues
B. kill disease-producing organisms in the body
C. increase the activity of white blood cells
D. induce the production of anti-bodies
9. Which of the following takes the shape of its container?
A. Chalk
B. Charcoal
C. Paper
D. Petrol
10. Which of the following substances reacts with ammonium chloride to produce ammonia gas?
A. Calcium hydroxide
B. Calcium chloride
C. Calcium carbonate
D. Calcium sulphate
11. The substance that sublimes when heated is
A. baking powder
B. camphor
C. common salt
D. sugar
Use the figure below to answer Questions 12 and 13
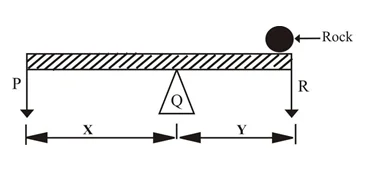
A rigid bar is balanced horizontally at a point by placing a rock on the bar as shown
12. Which of the parts labeled represents the pivot?
A. P B. Q C. R D. X
13. The effort is represented by
A. P B. Q C. R D. X
14. Gaps are left between railway lines to
A. prevent contraction
B. prevent rusting
C. allow for expansion
D. enable a train to stop
15. The structure which helps a fish to breathe under water is the
A. gill
B. air sac
C. operculum
D. mouth
16. Onions are planted by means of
A.bulbs
B.corms
C. suckers
D. rhizomes
17. The substance that enables green plants to trap sunlight for the manufacture of food is
A. chlorophyll
B. chloroplast
C. phloem
D. xylem
18. Which of these organs in humans releases carbon dioxide as a waste product?
A. Kidney
B. Liver
C. Lung
D. Skin
19. Exchange of gases takes place in the respiratory system through the
A. Bronchi
B. Lungs
C.nostrils
D. trachea
20. The taste of water changes when it is boiled because
A. heat is absorbed during boiling
B. evaporation takes place during boiling
C. air is lost during boiling
D. steam is produced during boiling
21. Boiling and chlorination are used in water purification to
A. kill germs
B. help suspended particles to settle
C. remove suspended particles
D. remove hardness of the water
22. An example of intensive system of poultry keeping is the
A. deep litter system
B. fold unit system
C. free range system
D. Free-running system
23. During drought, some plants dry out because of high
I. atmospheric temperature
II. humidity
III. rate of evaporation
Which of the statements above is/are correct?
A. III only
B. I and II only
C. I and III only
D. I, II and III
24. The practice of starting new organization in response to identified opportunities is termed
A. agribusiness
B. business enterprise
C. entrepreneurship
D. management
25. One advantage of friction is that it
A. enables cutting tools to be sharpened
B. increases the efficiency of machines
C. produces a lot of heat in machines
D. wears off the soles of shoes
26. An example of a disease vector is
A. earthworm
B. liver fluke
C. tapeworm
D. tick
27. An example of a derived quantity is
A. length
B. mass
C. time
D. velocity
28. In electronic circuits, LEDs are used to indicate the absence or presence of
A. emitter and collector
B. electric current
C. p-n junction
D. voltage source.
29. The organelle which occupies the largest portion of a plant cell is the
A. chloroplast.
B. mitochondrion.
C. nucleus.
D. vacuole.
30. Which of the following factors contribute to early parenthood?
I. Illiteracy
II. Poverty
III. Peer pressure
IV. Lack of parental care
A. I and II only
B. II and III only
C. III and IV only
D. I, II, III and IV
31. Plants lose water through a process called
A. photosynthesis
B. fertilization
C. transpiration
D. respiration
32. The process by which living things increase in number is referred to as
A. growth
B. development
C. reproduction
D. multiplication
33. Regular brushing of teeth is primarily done in order to
A. keep the mouth fresh
B. clear away food particles from the teeth
C. remove bad smell in the mouth
D. kill bacteria in the mouth
34. Friction is defined as a force which
A. accompanies motion
B. acts against motion
C. causes motion
D. makes motion easy
35. Which of the following organisms causes malaria?
A. Tsetsefly
B. Fungi
C. Virus
D. Plasmodium
36. The outer ear is also referred to as
A. cochlea
B. tympanum
C. pinna
D. incus
37. Trees in desert regions have thick barks which enables them to
A. prevent heat loss
B. absorb more light
C. prevent water loss
D. absorb more water
38. By the end of digestion, lean meat is turned into
A. amino acids
B. fatty acids
C. glycerol
D. glucose
39. Which of the following diseases affects the lungs?
A. Cholera
B. Measles
C. Tetanus
D. Tuberculosis
40. Which of the following structures regulate the amount of light that enters the eye?
A. Choroid
B. Cornea
C. Iris
D. Lens
INTEGRATED SCIENCE 1
OBJECTIVE TEST
ANSWERS
1. B mercury 2. B carbon dioxide 3. A other people collect drinking water from them 4. A Iron and Carbon 5. D pneumonia 6. B evaporation 7. D craters 8. D reduce the production of anti-bodies 9. D Petrol 10. A Calcium hydroxide 11. B camphor 12. B Q 13. A P 14. C allow for expansion 15. A gill 16. A bulbs 17. A chlorophyll 18. C lungs 19. B lungs 20. C air is lost during boiling 21. A kill germs
INTEGRATED SCIENCE 2
ESSAY
ANSWERS
(a) (i) The aim of the experiment [2 marks]
To determine the drainage ability / water-holding capacity of the soils (ii) Soil with the highest rate of drainage [1 mark] Soil K (iii) Soil with the highest water retention capacity [1 mark] Soil M (iv) The soil most likely to lose water and dry faster after rainfall [1 mark] Soil K (v) The soil most likely to be waterlogged after rainfall [1 mark] Soil M (vi) Which of the soil types would be suitable for maize cultivation? [1 mark] Soil L (b) (i) What each of the symbols labelled I, II, III and IV represent I – Danger II – Corrosive III – Highly inflammable / highly flammable IV – No naked flame (ii) One substance each that is associated with: (α) I; DDT, Hydrogen cyanide, Salicylic acid (β) II; Concentrated Inorganic acids, such as HCl, H2SO4, HNO3, Concentrated inorganic bases, such as NaOH, KOH, Ca(OH)2 Household bleach (γ) III. Petrol, Kerosene, LPG, Perfume, Insecticides, Alcohol [3 marks]
(iii) A place where the hazard symbol labelled IV is often displayed [1 mark] Gas Filling stations, Storage places of combustible substances (iv) Symbol(s) found on chemical containers [3 marks] I, II and III (c) (i) General name for the devices. [1 mark] Simple machines (ii) Identification of each of the devices labelled A, B, C and D. [4 marks] A – Wheel barrow B – Inclined plane C – Pulley D – Gear (iii) The parts labelled I, II and III of device A when it is considered as a lever. [3 marks] I – Effort II – Load III – Pivot (iv) What the arrow represents in the device labelled B [1 mark] Direction of effort / effort distance (v) The type of work done with each of the devices labelled: (α) C; Lifting objects (β) D; moving a vehicle or parts of an engine efficiently [2 marks]
(d) (i) Names of the parts labelled I, II, III, IV and V [5 marks] I – Stomach II – Small intestines III – Large intestines IV – Rectum V – Oesophagus / gullet (ii) The part(s) of the digestive system where (α) digestion of food substances occur I and II (β) digested food is absorbed into the bloodstream [3 marks] II (iii) The end-products of the digestion that is absorbed into the bloodstream [3 marks] Amino acids, glucose, fatty acids and glycerol
(a) (i) What is germination of seed?
The process by which a viable seed grows/develops into a seedling. (ii) State two conditions necessary for the germination of seed.
Presence of air
Presence of water
Viable seed
Optimum temperature
(b) State four methods used in identifying farm animals Tagging, tattooing, branding, tonging, ear notching (c) Explain why it is easier to cut a piece of yam with a sharp knife than with a blunt knife The cutting edge of a sharp knife has very small surface area so requires smaller force to yield the pressure needed to cut the yam – making cutting easy, but the cutting edge of a blunt knife has a relatively larger surface area so it needs a larger force to yield the pressure needed to cut the yam. (d) State three differences between a metal and a non-metal.
| Metals | Non-metals |
| Have high melting point | Have low melting point |
| Are lustrous | Are not lustrous |
| Are malleable | Are not malleable |
| Have high density | Have low density |
| Are ductile | Are brittle |
| Are good conductors of heat and electric current | Are poor conductors of heat and electric current |
- (a) (i) What is technology?
The use of scientific knowledge to solve problems in everyday life
Or
The application of scientific knowledge and methods to make life / work easier, faster and more comfortable
Or
The study, development, and application of devices, machines, and techniques for manufacturing and productive processes
(ii) State two differences between science and technology. [4 marks]
| SCIENCE | TECHNOLOGY |
| Aims at gaining knowledge about nature | Aims at applying scientific knowledge to solve problems |
| Focuses more on experimentation and analysis | Focuses more on synthesis of design |
| Mainly theory based | Mainly practical based |
| Generally cannot be used to solve everyday problems | Are generally used to solve everyday problems |
Likely 2023 BECE Integrated Science Mock With Full Answers
(b) Draw potassium atom and show the distribution of electrons in its shells.
[K = 19] [4 marks]
(c) What energy transformations take place in each of the following activities?
(i) Using a flashlight battery to produce light in a bulb.
Chemical energy → Electrical energy → Light energy and heat
(ii) Using a microphone to address a gathering. [4 marks]
Electrical energy→ Sound energy
(d) List three components of soil. [3 marks]
- Mineral matter / rock particles,
- organic matter/humus,
- water,
- air,
- micro-organisms
- (a) (i) Electromagnetism
Magnetism produced by an electric current
or:
The process of making a magnet using an electric current
(ii) Diagram showing how nail can be magnetized
(b) Symptoms of malaria
- fever
- body pains
- feeling cold or hot
- headache
- nausea
- lack of appetite [any three]
(c) Ways of keeping the environment clean
- Clearing choked gutters
- Clearing weedy areas
- Burying empty cans
- Covering rubbish bins
- Sweeping dirty areas
- Scrubbing toilets and bathrooms
(D) New Substance Formed
(i) Ammonia (NH3) and dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl);
NEW SUBSTANCE: Ammonium chloride (NH4Cl)
(ii) Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl);
NEW SUBSTANCE: Sodium chloride (NaCl) and water (H2O)
(iii) Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl).
NEW SUBSTANCE: Calcium chloride (CaCl2), Carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O)
- (a) (i) An opaque object does not allow light to pass through, whereas
A translucent object allows some amount of light to pass through diffusely.
(ii) Opaque – wooden or metallic materials, mirror, the earth, mammals, etc
Translucent – fabric, lightly-coloured water, oily spot on paper, frosted glass, etc
(b) (i) Importance of seed dispersal
- Enables plants to grow in other areas;
- Prevents the over-crowding of plants in one area
- Helps to reduce the rapid spread of plant diseases
- Prevents competition for soil nutrients among plants
(ii) FRUIT MODE OF DISPERSAL
Tridax, silk cotton, – Wind
Cowpea, Crotalaria, Balsam – Explosive Mechanism
Coconut, – Water
Orange, Guava, Tomatoes, Maize – Animals (man and others)
(c) (i) Recycling – The process of converting waste materials into new useful products
(ii) Advantages of recycling
- Employment / income generation for people
- Pollution of the environment by waste materials is reduced
- Reduction of resources for production
- Saving of money that would have been used for controlling waste
- Generation of energy for increased production [any two]
(iii) Recycled products in Ghana
Paper, biogas, polythene materials, rubber, particle boards, iron rods, etc. [any three]
- (a) (i) What is weather?
The atmospheric condition of a place at a particular time.
or
The state of the atmosphere at a particular place and time
or
The condition of the atmosphere of a place over a short period of time
(ii) State two differences between weather and season [4 marks]
| WEATHER | SEASON |
| Atmospheric condition of a place over a short period of time | The average atmospheric condition of a place over a longer period of time within a year |
| Changes relatively quickly (lasts for a short time, usually about a day) | Changes relatively slowly (lasts for a longer time, usually 3 or more months) |
| It is less predictable | It is more predictable |
(b) State the composition of each of the following alloys;
(i) steel;
iron and carbon
(ii) stainless steel [3 marks]
iron, carbon and chromium
(c) List four benefits of vegetables to humans [4 marks]
Provide mineral salts, which supports metabolic activities for proper functioning of the body
Provide vitamins for protection against diseases
Provide dietary fibre for easy bowel movement
Provide antioxidants, which fights stress and strengthen immune system
Makes our food tastier / more enjoyable
(d) Name each of the stages labelled I, II, III and IV [4 marks]
- – Pollination
- – Fertilization
- – Dispersion / dispersal
- – Germination

 Bimbilla: College of Education students leave campus as CETAG strike continues
Bimbilla: College of Education students leave campus as CETAG strike continues  Angie’s Leaked Tape: Angie Stylish Has Disgraced Konongo Odumase School – School Mate Angrily Speaks
Angie’s Leaked Tape: Angie Stylish Has Disgraced Konongo Odumase School – School Mate Angrily Speaks  1st STEM College of Education in Ghana: Bawumia cuts sod for construction
1st STEM College of Education in Ghana: Bawumia cuts sod for construction  Stop denying students exeat; NAGRAT to SHS Heads
Stop denying students exeat; NAGRAT to SHS Heads  BECE; Four Teachers caught up for assisting students- WAEC
BECE; Four Teachers caught up for assisting students- WAEC  North Tongu District BECE Candidates prevented from wearing shoes or belts
North Tongu District BECE Candidates prevented from wearing shoes or belts  Bawumia’s smartphone pledge misguided and visionless – Adongo
Bawumia’s smartphone pledge misguided and visionless – Adongo  Good Grow: The Marijuana Farm Founded by Akufo-Addo’s Daughters
Good Grow: The Marijuana Farm Founded by Akufo-Addo’s Daughters  National Food Suppliers for Free SHS set to picket at Education Ministry
National Food Suppliers for Free SHS set to picket at Education Ministry  Information Ministry justifies ¢151k paid to staff as Covid-19 risk allowance
Information Ministry justifies ¢151k paid to staff as Covid-19 risk allowance